This article was generated with the help of Chat GPT!
Capacitor
A capacitor is an essential electronic component used in various circuits to store and release electrical energy. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as the dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the capacitor, it stores electrical charge on its plates.
Capacitance
The capacitance of a capacitor determines its ability to store charge. It is measured in Farads (F). One Farad is a very large unit of capacitance, so capacitors are typically expressed in microfarads (μF) or picofarads (pF). Capacitors come in a wide range of capacitance values, from a few picofarads to thousands of microfarads.
Charging and Discharging
When a voltage is applied across the capacitor, the plates accumulate opposite charges, with one plate becoming positively charged and the other negatively charged. This process is known as charging the capacitor. The rate at which the capacitor charges depends on its capacitance and the resistance in the circuit.
When the voltage is removed, the capacitor starts to discharge, releasing the stored charge back into the circuit. The time it takes for the capacitor to discharge is determined by its capacitance and the resistance in the circuit.
ٍCapacitor Symbol
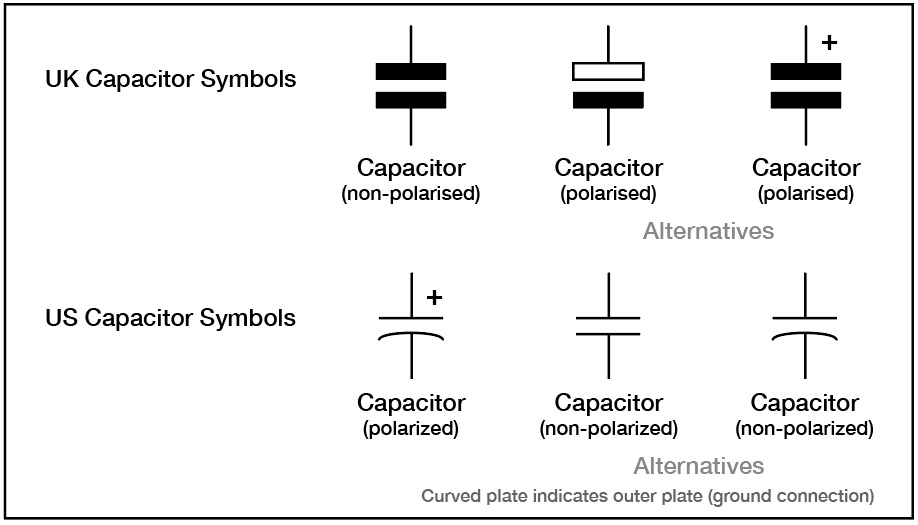
Capacitor Symbols
The symbol for a capacitor consists of two parallel lines representing the plates and an adjacent curved line, indicating the dielectric material between them.
Types of Capacitors
There are various types of capacitors, each with its own characteristics and applications:
- Ceramic Capacitors: These are compact and inexpensive capacitors used in a wide range of applications.
- Electrolytic Capacitors: They are polarized capacitors suitable for higher capacitance values and are commonly used in power supply circuits.
- Tantalum Capacitors: These are small and reliable capacitors often used in electronic devices and circuits.
- Film Capacitors: Film capacitors are known for their stability, and they come in different types like polyester, polypropylene, and metalized film capacitors.
- Variable Capacitors: These capacitors have adjustable capacitance and are used in tuning circuits and radio frequency (RF) applications.
- Supercapacitors: Also known as ultracapacitors, they have high capacitance values and can store and release a large amount of energy quickly.
Applications
Capacitors are used in various electronic and electrical applications, including:
- Decoupling and Filtering: Capacitors help stabilize voltage and filter out noise in power supply circuits.
- Timing Circuits: Capacitors are used in conjunction with resistors to create time delays and oscillators.
- Coupling and Bypassing: Capacitors couple AC signals between stages of amplifiers and bypass AC signals to the ground.
- Energy Storage: Capacitors are used in energy storage systems, flashlights, and camera flashes.
- Motor Start and Run: Capacitors help in starting and running electric motors.
- Audio Applications: Capacitors are used in audio circuits for coupling, filtering, and impedance matching.
Conclusion
Capacitors play a crucial role in electronics, providing essential functions such as energy storage, filtering, and timing. With their wide range of types and applications, capacitors are fundamental components in various electronic devices and circuits, making them indispensable in modern technology.