Introduction to BJT transistors
Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) are three-terminal semiconductor devices that can be used as amplifiers or switches. BJTs are made of two types of semiconductor material: n-type and p-type. The n-type material has an excess of electrons, while the p-type material has a deficiency of electrons.
The three terminals of a BJT are the base, emitter, and collector. The base is the control terminal, and the emitter and collector are the output terminals. When a small current is applied to the base, it can cause a much larger current to flow between the emitter and collector. This is how BJTs can be used as amplifiers.
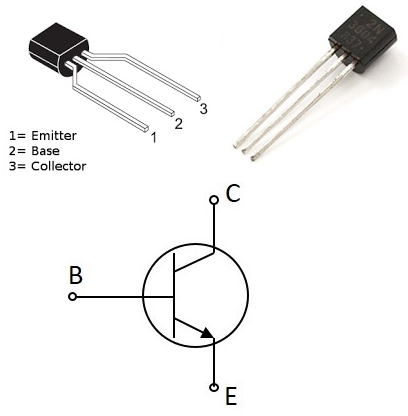
BJT Transistor (NPN)
BJTs are also used as switches. When the base current is turned off, the collector current is also turned off. This makes BJTs ideal for applications where a small current can be used to control a large current.
Types of BJT transistors
There are two main types of BJT transistors: NPN and PNP. NPN transistors have an n-type base, an n-type emitter, and a p-type collector. PNP transistors have a p-type base, a p-type emitter, and an n-type collector.
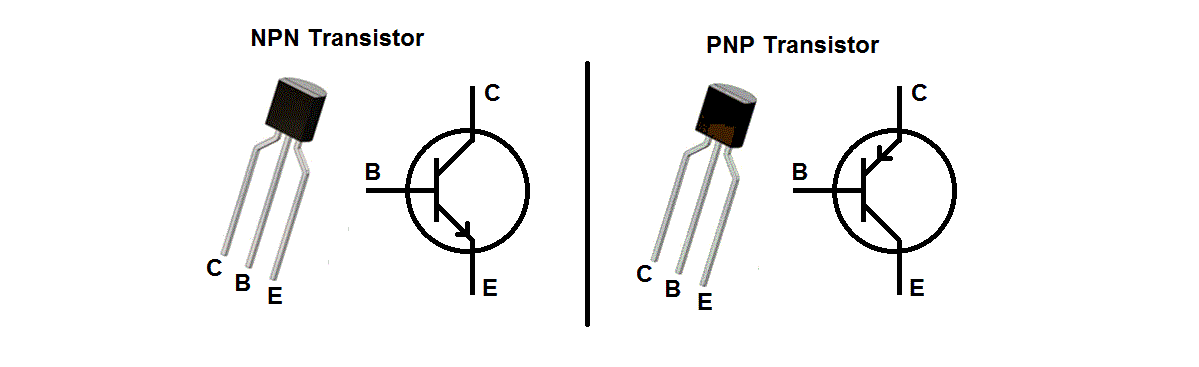
NPN & PNP Transistors
Applications of BJT transistors
BJT transistors are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Amplifiers
- Switches
- Oscillators
- Logic gates
- Comparators
- Buffers
- Linearizers
Biasing of BJT transistors
In order for a BJT transistor to work properly, it must be biased. Biasing means applying a small current to the base to ensure that the transistor is always in either the on or off state. There are two main types of biasing:
- Forward biasing
- Reverse biasing
Forward biasing is when the base-emitter junction is forward biased. This means that the positive terminal of the voltage source is connected to the base, and the negative terminal of the voltage source is connected to the emitter.
Reverse biasing is when the base-emitter junction is reverse biased. This means that the positive terminal of the voltage source is connected to the emitter, and the negative terminal of the voltage source is connected to the base.
Characteristics of BJT transistors
There are several important characteristics of BJT transistors, including:
- Current gain
- Voltage gain
- Input impedance
- Output impedance
- Switching speed
Current gain is the ratio of the collector current to the base current. Voltage gain is the ratio of the change in collector voltage to the change in base voltage. Input impedance is the resistance to the flow of current into the base. Output impedance is the resistance to the flow of current out of the collector. Switching speed is the time it takes for a BJT transistor to switch from the on state to the off state, or vice versa.
Troubleshooting BJT transistors
If a BJT transistor is not working properly, there are a few things that you can check:
- Make sure that the transistor is properly biased.
- Check the connections to the transistor.
- Check the transistor for damage.
If you have checked all of these things and the transistor is still not working properly, then you may need to replace it.